Researchers in the United States claim to have established a convincing statistical link between gun ownership and homicide, according to a study published Thursday.
The study, which appears in the American Journal of Public Health, challenges the National Rifle Association's claim that increased gun ownership does not lead to higher levels of gun violence.
 Full Story
Full Story
Early childhood deaths around the world have been cut in half since 1990 but some 18,000 children under five still die every day, according to a new report out Friday.
Around 6.6 million children perished before their fifth birthday last year, compared to 12.6 million in 1990, said the report by UNICEF, the World Bank and the World Health Organization.
 Full Story
Full Story
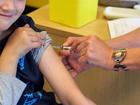
Health officials say 2013 already is one of the worst years for measles in the U.S. in more than 15 years.
Before a vaccine became available about 50 years ago, nearly all children got measles by their 15th birthday. In those days, nearly 500 Americans died from measles each year.
 Full Story
Full Story
A new test -- looking at three genes -- could predict which prostate cancers will turn aggressive, helping avoid invasive treatments for those that will grow more slowly, a study out Wednesday said.
Used alongside existing tests, the analysis will help doctors determine whether treatment is needed or if "active surveillance" would suffice, Columbia University researchers said in the study in "Science Translational Medicine."
 Full Story
Full Story
Scientists in Spain said on Wednesday they had made mature cells in living mice revert to their youthful, versatile state, in a step toward the goal of tissue regeneration by stem cells.
Right now, the technique is at its earliest stage and is hedged with safety questions, which makes it impossible to envisage in humans.
 Full Story
Full Story
Many middle-aged men find their waistlines expanding and their sex drive shrinking, symptoms a new study out Wednesday suggests can be traced to a hormone deficiency -- but not the one you might imagine.
Previously, a drop in testosterone production might have been suspected as the culprit, but researchers said a decline in estrogen may be part of the problem.
 Full Story
Full Story
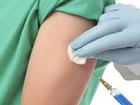
A new vaccine being rolled out in the "meningitis belt" that stretches across north-central Africa has reduced cases of the potentially fatal disease by 94 percent, doctors reported on Thursday in The Lancet.
Researchers monitored the spread of type A meningococcal disease in Chad after the new vaccine, MenAfriVac, had been approved by world health watchdogs in 2010.
 Full Story
Full Story
Somali-born activist and former supermodel Waris Dirie on Wednesday opens a center in Germany to treat victims of female genital mutilation, which she was subjected to as a child.
About 8,000 young girls are circumcised every day in Africa and the Middle East, and the Desert Flower Medical Center, located in a Berlin hospital, will offer reconstructive surgery and psychological help to those among the 50,000 girls and women in Germany who need it.
 Full Story
Full Story
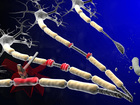
New research suggests it might be possible to spot early signs of multiple sclerosis in patients' spinal fluid, findings that offer a new clue about how this mysterious disease forms.
The study released Tuesday was small and must be verified by additional research. But if it pans out, the finding suggests scientists should take a closer look at a different part of the brain than is usually linked to MS.
 Full Story
Full Story
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has issued a positive review of a breast cancer drug from Roche that could soon become the first pharmaceutical option approved for treating early-stage disease before surgery.
In documents posted online, FDA scientists said women who received the drug Perjeta as initial treatment for breast cancer were more likely to be cancer-free at the time of surgery than women who received older drug combinations. Although the results come from mid-stage trials of the drug, FDA scientists recommended accelerating approval of the drug.
 Full Story
Full Story



